Exact Method for Finding f
The Method
With this method we perform the following experiment three times, with different values of a. This leads to three distinct values of d:
- Take the lens off the camera body.
- Locate an opaque object at a relatively close distance.
- Place a light source behind the object.
- Position the lens in the shadow of the object.
- Turn the front element of the lens towards the object.
- Place a white piece of paper behind the rear element of the lens, perpendicular to the lens axis. This paper will be used as a screen that shows the image that the lens projects.
- Move the paper back and forth until the image of the bright object is in focus.
- Measure the distance a between the object and the front-most point of the lens.
- Measure the distance d between the rear-most point of the lens mount and the projected image.
Figure 1 illustrates.
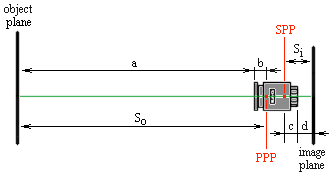
Figure 1.
Now without refocusing the lens, repeat the above experiment with a’ > a. Measure the distance d’. Repeat once again, with a” > a’, and measure d”.
Now we need to solve the following system of three equations and three unknowns:
| 1 1 1
| ----- + ----- = - (7)
| a + b c + d f
|
| 1 1 1
| ------ + ------ = - (8)
| a' + b c + d' f
|
| 1 1 1
| ------ + ------ = - (9)
| a" + b c + d" f
Since the right sides of equations (7) and (8) are equal, their left sides must be equal too:
1 1 1 1
----- + ----- = ------ + ------ <=>
a + b c + d a' + b c + d'
a + b + c + d a' + b + c + d'
-------------- = ---------------- <=>
(a + b)(c + d) (a' + b)(c + d')
(a + b + c + d)(a'c + a'd' + bc + bd') =
(a' + b + c + d')(ac + ad + bc + bd) <=>
aa'c + aa'd' + abc + abd' + a'bc + a'bd' + bbc + bbd' +
a'cc + a'cd' + bcc + bcd' + a'cd + a'dd' + bcd + bdd' =
aa'c + aa'd + a'bc + a'bd + abc + abd + bbc + bbd +
acc + acd + bcc + bcd + acd' + add' + bcd' + bdd' <=>
We cancel the terms aa’c, abc, a’bc, bbc, bcc, bcd’, bcd and bdd’ from both sides, then factor out in the following way:
aa'(d' - d) + ab(d' - d) + a'b(d' - d) + bb(d' - d) =
cc(a - a') + cd'(a - a') + cd(a - a') + dd'(a - a') <=>
(aa' + ab + a'b + bb)(d' - d) = (cc + cd' + cd + dd')(a - a') <=>
(a + b)(a' + b)(d' - d) = (c + d)(c + d')(a - a') (10)
Performing similar manipulations with equations (7) and (9), we get:
(a + b)(a" + b)(d" - d) = (c + d)(c + d")(a - a") (11)
Now we divide (19) into (11), and solve for b:
(a' + b)(d' - d) (c + d')(a - a') ---------------- = ---------------- <=> (a" + b)(d" - d) (c + d")(a - a") (a'd' - a'd + bd' - bd)(ac - a"c + ad" - a"d") = (a"d" - a"d + bd" - bd)(ac - a'c + ad' - a'd') <=> aa'cd' - a'a"cd' + aa'd'd" - a'a"d'd" + - aa'cd + a'a"cd - aa'dd" + a'a"dd" + abcd' - a"bcd' + abd'd" - a"bd'd" + - abcd + a"bcd - abdd" + a"bdd" = aa"cd" - a'a"cd" + aa"d'd" - a'a"d'd" + - aa"cd + a'a"cd - aa"dd' + a'a"dd' + abcd" - a'bcd" + abd'd" - a'bd'd" + - abcd + a'bcd - abdd' + a'bdd' <=>
We cancel the terms a’a”d’d”, a’a”cd, abd’d” and abcd from both sides, then move all terms involving b to the left side, all others to the right, and factor out in the following way:
b [ac(d' - d") + a"c(d - d') + a"d"(d - d') +
ad(d' - d") + a'c(d" - d) + a'd'(d" - d)] =
aa'c(d - d') + a'a"c(d' - d") + a'a"d(d' - d") +
aa"c(d" - d) + aa'd"(d - d') + aa"d'(d" - d) <=>
b [a(c + d)(d' - d") + a"(c + d")(d - d') + a'(c + d')(d" - d)] =
aa'(c + d")(d - d') + a'a"(c + d)(d' - d") + aa"(c + d')(d" - d) <=>
a'a"(c + d)(d' - d") + aa"(c + d')(d" - d) + aa'(c + d")(d - d')
b = ---------------------------------------------------------------- (12)
a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')
To help our further calculations, we calculate the expression a + b:
aa(c + d)(d' - d") + aa'(c + d')(d" - d) + aa"(c + d")(d - d') +
a'a"(c + d)(d' - d") + aa"(c + d')(d" - d) + aa'(c + d")(d - d')
a + b = ----------------------------------------------------------------
a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')
(aa + a'a")(c + d)(d' - d") +
a(a' + a")(c + d')(d" - d) +
a(a' + a")(c + d")(d - d')
a + b = ----------------------------------------------------------- <=>
a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')
(aa + a'a")(c + d)(d' - d") +
a(a' + a")(cd" - cd + d'd" - dd' + cd - cd' + dd" - d'd")
a + b = ----------------------------------------------------------- <=>
a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')
(aa + a'a")(c + d)(d' - d") + a(a' + a")(c + d)(d" - d')
a + b = ----------------------------------------------------------- <=>
a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')
(aa + a'a" - aa' - aa")(c + d)(d' - d")
a + b = ----------------------------------------------------------- <=>
a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')
(a - a")(a - a')(c + d)(d' - d")
a + b = ----------------------------------------------------------- (13)
a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')
Using similar transformations, we simplify the expression a’ + b:
(a - a')(a" - a')(c + d')(d" - d)
a + b' = ----------------------------------------------------------- (14)
a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')
Now we substitute (13) and (14) into equation (10), cancel out the terms (a – a’)(c + d)(c + d’) from both sides, then solve for c:
(a - a")(d' - d")(a - a')(a" - a')(d" - d)(d' - d) --------------------------------------------------------------- = 1 [a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d')]^2 a(c + d)(d' - d") + a'(c + d')(d" - d) + a"(c + d")(d - d') = sqrt[(a - a")(d' - d")(a - a')(a" - a')(d" - d)(d' - d)] (15) ac(d' - d") - a'c(d - d") + a"c(d - d') + ad(d' - d") - a'd'(d - d") + a"d"(d - d') = sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] c[a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')] = sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] + - ad(d' - d") + a'd'(d - d") - a"d"(d - d') <=> sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] + - ad(d' - d") + a'd'(d - d") - a"d"(d - d') c = ---------------------------------------------------------- (16) a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')
At this point we can start solving for f. First we express the quantity c + d:
sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] +
a'd'(d - d") - a"d"(d - d') - a'd(d - d") + a"d(d - d')
c + d = ----------------------------------------------------------
a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')
sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] +
a'(d' - d)(d - d") - a"(d" - d)(d - d')
c + d = ----------------------------------------------------------
a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')
sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] +
(a" - a')(d - d')(d - d")
c + d = ---------------------------------------------------------- (17)
a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')
We note that the denominator of equation (13) is the same as the left side of equation (15). So we rewrite (13), and then substitute the result into (7):
sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] 1 1
-------------------------------------------------------- + ----- = -
(a - a")(a - a')(c + d)(d' - d") c + d f
1 sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] +
(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d")
- = ----------------------------------------------------------
f (a - a")(a - a')(c + d)(d' - d")
(a - a")(a - a')(c + d)(d' - d")
f = ---------------------------------------------------------- (18)
sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] +
(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d")
Now we substitute (17) into (18), and simplify:
(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d"){(a" - a')(d - d')(d - d") +
sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")]}
f = ---------------------------------------------------------------- <=>
{sqrt[(a" - a')(a" - a)(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")] +
(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d")}[a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')]
(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d")sqrt[(a" - a')(d - d')(d - d")]
{sqrt[(a" - a')(d - d')(d - d")] + sqrt[(a" - a)(a' - a)(d' - d")]}
f = ---------------------------------------------------------------------
[a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')]sqrt[(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d")]
{sqrt[(a" - a')(d - d')(d - d")] + sqrt[(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d")]}
(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d")sqrt[(a" - a')(d - d')(d - d")]
f = ---------------------------------------------------------------------
[a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')]sqrt[(a - a")(a - a')(d' - d")]
__________________________________________________
\/(a" - a)(a" - a')(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")
f = ---------------------------------------------------- .
a(d' - d") - a'(d - d") + a"(d - d')
Finally, with a great sigh of relief, we substitute (13) and (15) into (6), and solve for M:
(c + d)sqrt[(a" - a)(a" - a')(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")(d' - d")]
M = --------------------------------------------------------------- <=>
(c + d)(a" - a)(a' - a)(d' - d")
sqrt[(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")]
M = ------------------------------- <=>
sqrt[(a" - a)(a' - a)(d' - d")]
_ ________________________
| /(a' - a)(d - d')(d - d")
M = | / ------------------------ .
|/ (a" - a)(a' - a)(d' - d")
Method Evaluation
The method has three main merits:
- It is exact.
- The focal length can be calculated also when the lens is set to infinity.
- The measurements that it relies on are simple to execute.
At the same time, two main drawbacks should be pointed out:
- There are more measurements to make compared to the other methods.
- Measurement errors become even more significant than the previous methods because their values are multiplied together.